you should explain how to do it step by step to a 2nd grader
- Get better
- Understand it
- I totally understand this and it’s not like I have no idea how to do multivariable calculus
Right, we would never think that
I’ve seen this happen multiple times after reading this post a few weeks ago.
If mysz wrote code, he would be writing way better code than anything I could ever make. All this math y’all are talking about is above my level lol
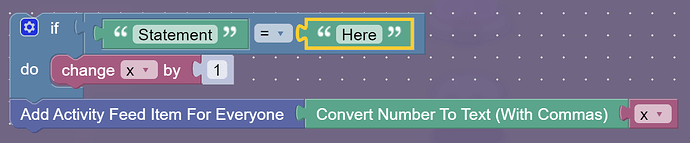
Ok so I just found a cool memory save. It’s not enough information to make it’s own post, so I decided to just tack it on here. If you want to set a varible to 0 if something is false, and to 1 if something is true, this code works:
Because Blockly auto sets all varibles to 0, this will set x to 1 if the statement is true, and set x to 0 if the statement is false. Just a quick way to save 2 blocks!
noice
Should we make a new line of guides, like [ ![]() PSA! ] and [
PSA! ] and [ ![]() Resources ], called [
Resources ], called [ ![]() Mini-Guide ]? It would be useful for information we thought was too short to make its own guide.
Mini-Guide ]? It would be useful for information we thought was too short to make its own guide.
- Yes
- No
0 voters
What would you like to know? I’m kind of bored right now, and want to pull a @Zypheir(Create a detailed description of something).
Ok, explain big f’s in math with the d/dx and d/dy (that was silly, I mean integrals). Technically, d/dx simplifies to 1/x ![]()
Any “hardest” Algebra 2 concept, can’t be that hard…
I know, but I can’t watch any of my YT front page without knowing what integrals are…
I have to skip so many minutes (my home page is VERY different)
TLDR; Integrals use infinitesimally small areas summed up to approximate area.
Think of it like this. The curve f(x) = x^2. You can’t find the area of a curve, right? But you can approximate it with infinitely small area. This is called a definite integral.
It’s the rectangles but then you make them this small ![]() .
.
“![]() ”
”
You can use the fundamental theorem of calculus to calculate definite integrals.
An integral from a to b of f’(x) is F(b) - F(a) (The antiderivative of the function at points b and a).
I would suggest Khan Academy or Organic Chemistry- I’m not a good explainer.
Organic Chemistry Tutor is the W’est channel on YT.
Contradicting details…
Yeah. With Riemann Sums you can partition small rectangles randomly. As long as the max-area rectangle, Δxf(xi) is approaching 0, you can approximate the area under a curve.
Integrals are fundamental to calculus, and in Multivariable calculus, there are double integrals, triple integrals, line integrals, surface integrals, volume integrals, etc.
What are you even going to do with this knowledge?